班级所有同学去参观自然博物馆,在博物馆前列队完毕后解散进入馆内自由参观。活动结束后,领队老师想恢复参观前队列的次序,但是在解散前老师并没有记录下来所有人的次序,幸运的是每个人都知道在队列里自己的下一个人是谁,领队老师也知道队列里第一个人是谁。根据这些信息其实可以还原参观前的队列。
一、链表的定义
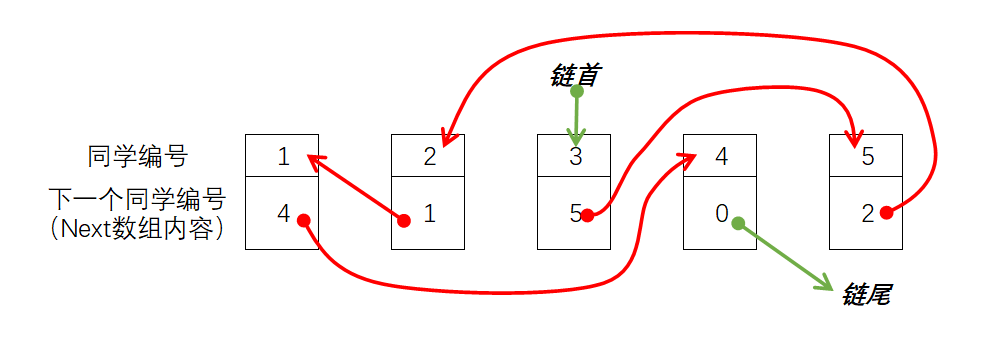
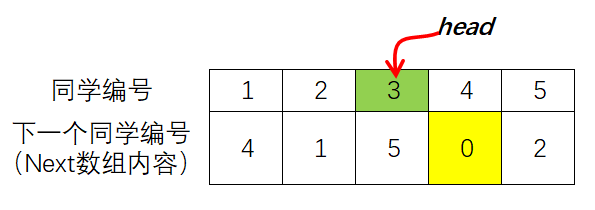
假设\(n\)位同学的编号依次为\(1~n\),用一个int数组Next记录下最初队列里每个人的下一个人的编号(也就是编号为\(i\)的同学的下一个人的编号保存在数组元素Next[i]中),假设队列第一个人的编号是head,那么可知第二个人的编号是Next[head],第三个人的编号是Next[Next[head]]…如果将最后一个人的下一个人编号设置为特殊值0(表示后面没人了),很显然可以通过循环结构依次找到最初队列的每个人来恢复队列:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5;
int Next[N+1] = {0,4,1,5,0,2};
int head = 3;
int main()
{
for(int i=head;i!=0;i=Next[i]){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
根据上面的例子可知:如果知道每个元素的后一个元素(或者前一个元素),那么可以恢复整个排列顺序。利用上面的方式存储元素排列顺序的线性表,称为链表(list)。
二、普通链表
有同学可能会想到,直接使用原始数组也能解决问题呀,那么为什么要使用链表呢?我们来看新的问题:如果\(n\)位同学排好了队,现在有一位编号为\(y\)同学要插到编号为\(x\)的同学后面。直接使用数组需要将数组末尾最后一个元素反向到第\(x+1\)个元素全部后移一位,然后将编号\(y\)插入到数组下标\(x+1\)处。同样地,队列里某个同学要从队列里出来,要删除数组中的元素,又会导致数组内部大量元素前移。可知不管是插入还是删除元素,直接用原始数组操作会出现大量元素移动操作,导致效率低下。
1.链表的使用
如果使用链表呢?还是上面图例中的情况,假设在编号1的同学后要插入一个编号为6的同学,那么操作前后图示如下:

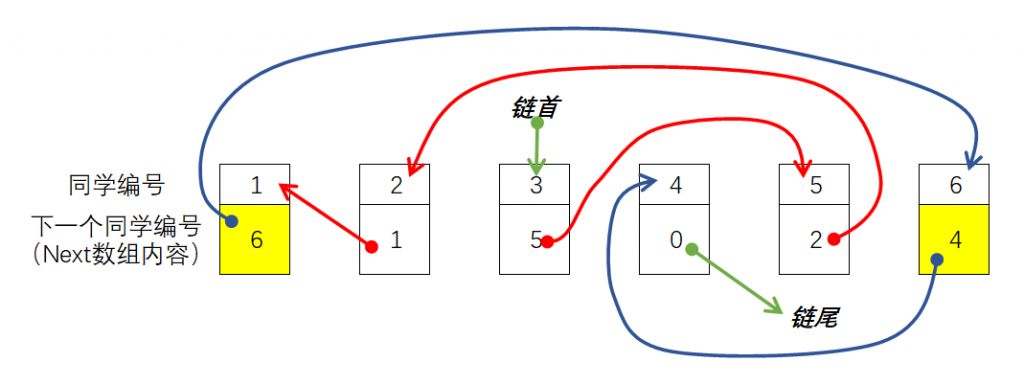
将编号为\(y=6\)的元素插入到链表编号为\(x=1\)的元素的后面,由图可知,只需要执行:Next[y] = Next[x];Next[x] = y;
如果要删除编号\(x=5\)的元素的下一个元素,那么操作前后图示如下:
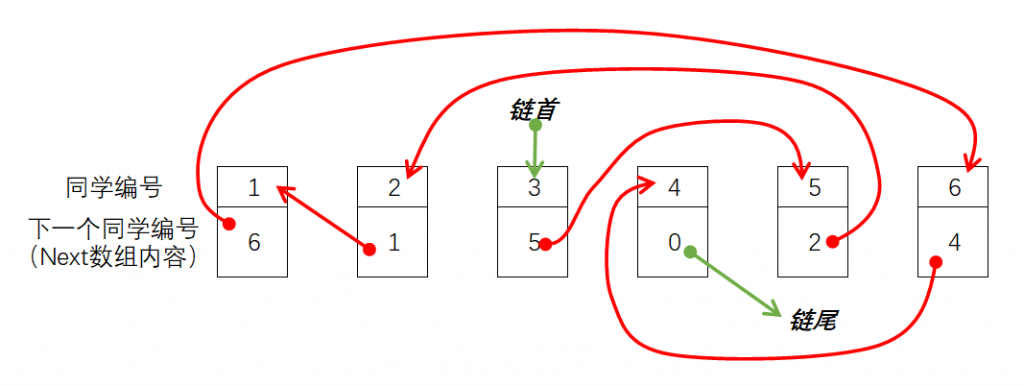
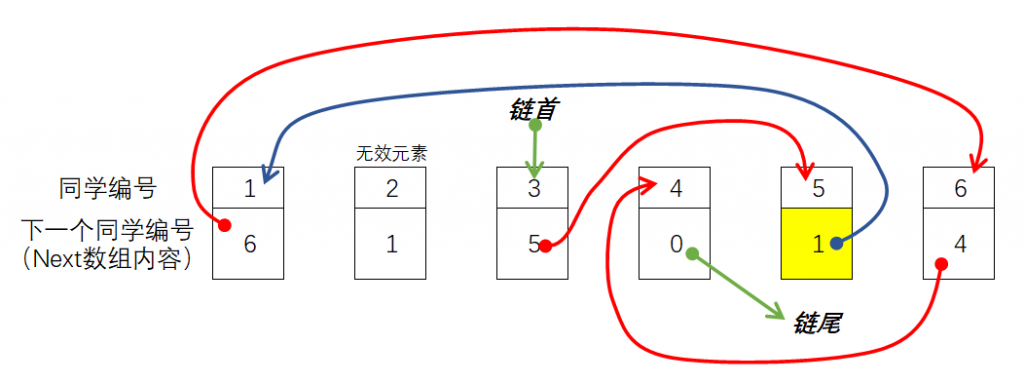
由图可知,由于Next[x]是编号为x的元素的下一个元素的编号,Next[Next[x]]是编号为x的元素的下下个元素的编号(其实就是删除x的下一个元素后,x的下一个元素的编号),那么删除编号为x的元素的下一个元素只需要执行Next[x] = Next[Next[x]]即可。
通过上面的分析可知,使用链表结构,可以轻松避免使用原始数组插入、删除元素时出现大量元素移位的情况,时间复杂度为\(O(1)\)。但是如果要查找链表第\(x\)个元素,那么需要从链首开始依次向后“顺蔓摸瓜”一样查找,时间复杂度为\(O(n)\),而可以随机存取的数组直接使用x下标即可。
2.使用链表解决约瑟夫问题
再来看约瑟夫问题,可以用链表来解决,用数组存储每个人的下一个人的编号,第 i 个人的下一个人的编号是 i+1,最后一个人的的下一个人的编号设置为 1,这样可以构成一个循环链表。数到 m 的人从链表里删除,也就是将数 m-1 的人的下一个人从链表里删除:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Next[1010];
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
Next[i] = i+1;
}
Next[n] = 1;
int p = n;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
//数(m-1)次
for(int j=1;j<m;j++){
p = Next[p];
}
//那么Next[p]数m
cout<<Next[p]<<" ";
//从链表删除Next[p]
Next[p] = Next[Next[p]];
}
return 0;
}
将约瑟夫问题变形:除了输入n和m,还要输入n个人的姓名,输出时除了输出编号,还要输出姓名。这个时候可以使用结构体数组来存储链表,结构体中使用成员变量name来记录姓名,使用成员变量next来记录下一个人的编号。
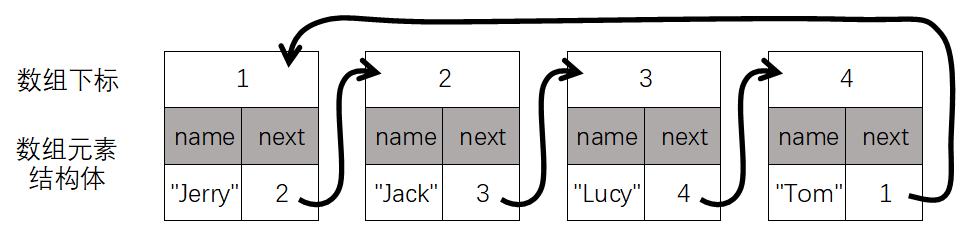
//不使用结构体
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Next[1010];
string name[1010];
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>name[i];
Next[i] = i+1;
}
Next[n] = 1;
int p = n;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
//数(m-1)次
for(int j=1;j<m;j++){
p = Next[p];
}
int q = Next[p];
cout<<q<<" "<<name[q]<<endl;
//从链表删除q
Next[p] = Next[q];
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Person{
string name;
int next;
};
Person list[1010];
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>list[i].name;
list[i].next = i+1;
}
list[n].next = 1;
int p = n;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
//数(m-1)次
for(int j=1;j<m;j++){
p = list[p].next;
}
int q = list[p].next;
cout<<q<<" "<<list[q].name<<endl;
//从链表删除q
list[p].next = list[q].next;
}
return 0;
}
三、双向链表
上面的问题都涉及到将元素插入到指定元素的后面,删除指定元素后面的元素,如果要插入到指定元素的前面,或者删除指定元素呢?这个时候可以使用双向链表:链表的每个元素可以设置成一个结构体,链表所有元素存储在结构体数组中;结构体里有基本数据成员(例如上面例子中的编号)、用来记录链表元素的下一个元素在数组中存储下标的next成员,此外再添加一个用来记录链表元素的上一个元素在数组中存储下标的prev成员;实际操作时,可以将链首元素存储在数组的首部:
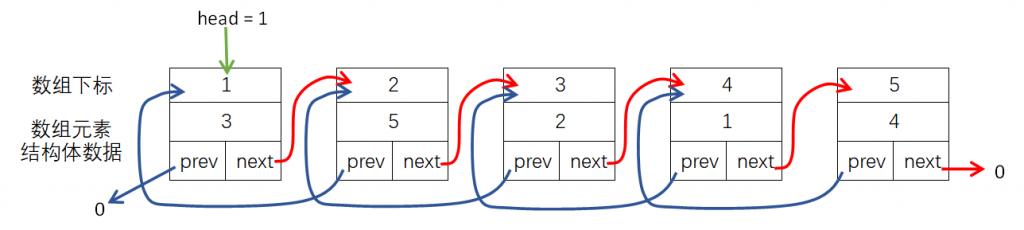
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000;
struct node{
int key;
int prev,next; //链表中:本元素的上一个元素、下一个元素在数组list中的下标
node(){}
node(int key,int prev,int next){
this->key = key;
this->prev = prev;
this->next = next;
}
};
node list[N+10]; //链表的所有元素存储在数组中
int tot = 0; //记录list数组实际存储数量
int head = 1; //链首“指针”(链表第一个元素在数组list中的存储下标)
void printall(){ //“顺蔓摸瓜”从链首遍历链表所有元素
int now = head;
while(now){
cout<<list[now].key<<" ";
now = list[now].next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
//生成上面图例的双向链表
list[++tot] = node(3,0,2);
list[++tot] = node(5,1,3);
list[++tot] = node(2,2,4);
list[++tot] = node(1,3,5);
list[++tot] = node(4,4,0);
printall();
return 0;
}
1.查找元素
查找链表结点key为x的元素在数组list中的存储下标(没找到会返回0):
int find(int x){
int now = head;
while(now && list[now].key!=x)
now = list[now].next;
return now;
}
如果用一个tail来记录链尾,还可以实现从链尾反向查找:
int rfind(int x){
int now = tail;
while(now && list[now].key!=x)
now = list[now].prev;
return now;
}
2.插入元素
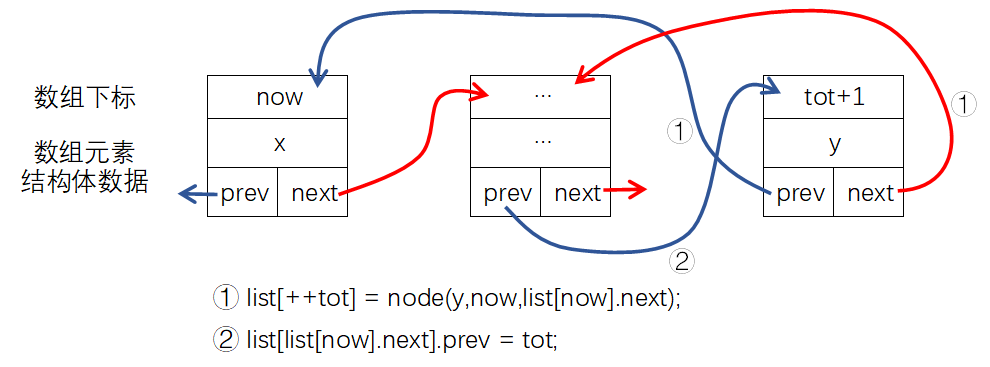
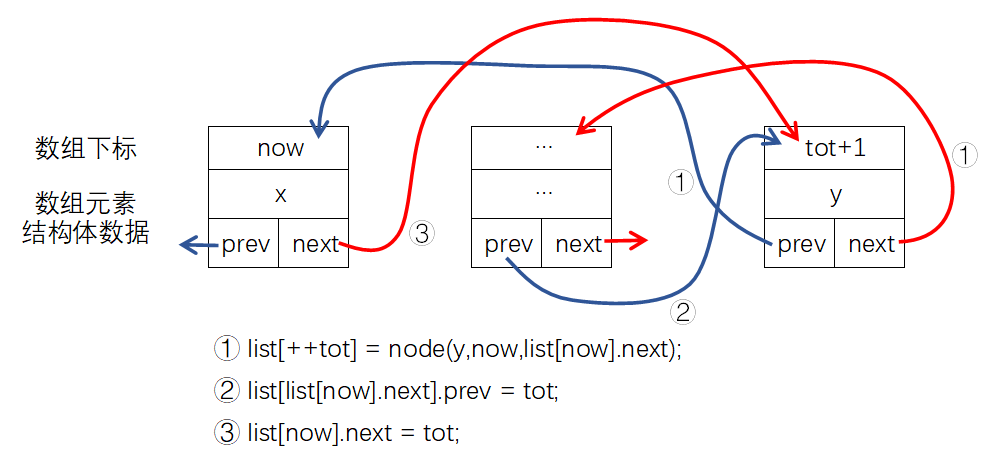
在key为x的元素后插入key为y的元素:
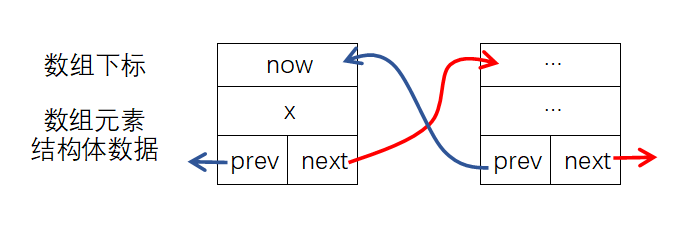
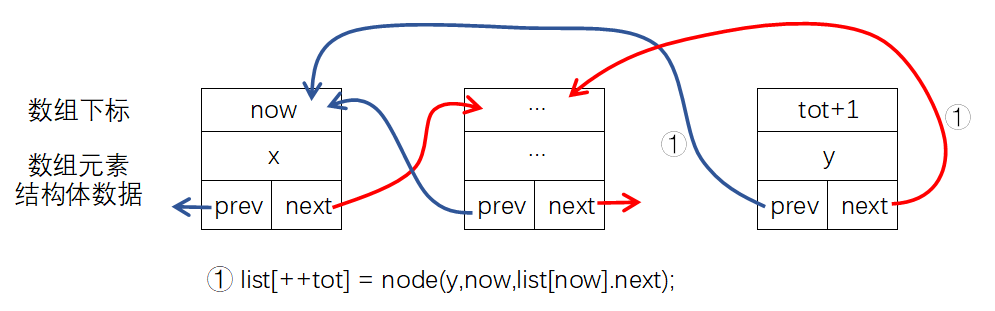
bool insert_back(int x,int y){
if(tot+1>N) return false;
int now = find(x);
if(now==0) return false; //未找到key为x的元素,插入失败
//查找结束后,list[now]是key为x的元素
//新元素存放到数组中
list[++tot] = node(y,now,list[now].next);
//更新list[now]下一个元素list[list[now].next]的prev
//list[now].next是list[now]的下一个元素在list数组的存储下标
//list[list[now].next]就是list[now]的下一个元素
list[list[now].next].prev = tot;
//更新list[now]的next
list[now].next = tot;
return true;
}
在key为x的元素前插入key为y的元素(图例分析略):
bool insert_front(int x,int y){
if(tot+1>N) return false;
int now = find(x);
if(now==0) return false; //未找到key为x的元素,插入失败
//查找结束后,list[now]是key为x的元素
//新元素存放到数组中
list[++tot] = node(y,list[now].prev,now);
//更新list[now]上一个元素list[list[now].prev]的next
//list[now].prev是list[now]的上一个元素在list数组的存储下标
//list[list[now].prev]就是list[now]的上一个元素
list[list[now].prev].next = tot;
//更新list[now]的prev
list[now].prev = tot;
if(head==now) head = tot;
return true;
}
3.删除元素
删除key为x的元素:
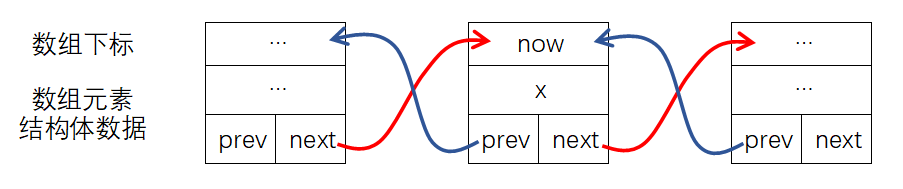


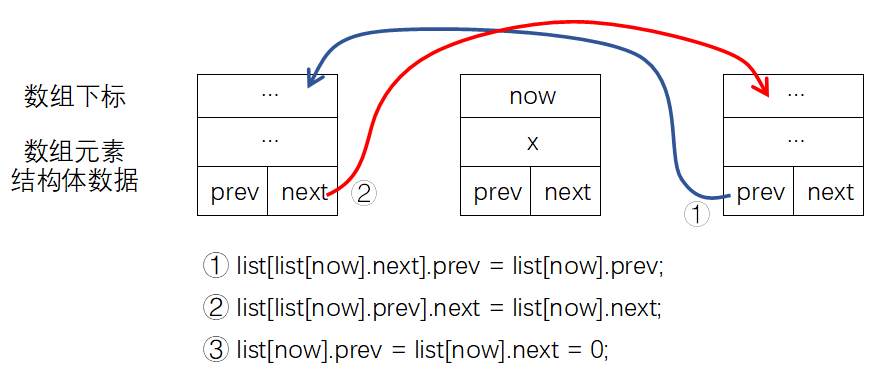
bool del(int x){
int now = find(x);
if(now==0) return false; //未找到key为x的元素,删除失败
//查找结束后,list[now]是key为x的元素
list[list[now].next].prev = list[now].prev;
list[list[now].prev].next = list[now].next;
if(head==now) head = list[head].next;
return true;
}
4.完整测试程序
完整双链表测试程序如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000;
struct node{
int key;
int prev,next; //链表中:本元素的上一个元素、下一个元素在数组list中的下标
node(){}
node(int key,int prev,int next){
this->key = key;
this->prev = prev;
this->next = next;
}
};
node list[N+10]; //链表的所有元素存储在数组中
int tot = 0; //记录list数组实际存储数量
int head = 1; //链首“指针”(链表第一个元素在数组list中的存储下标)
//“顺蔓摸瓜”从链首遍历链表所有元素
void printall(){
int now = head;
while(now){
cout<<list[now].key<<" ";
now = list[now].next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//查找链表结点key为x的元素在数组list中的存储下标
int find(int x){
int now = head;
while(now && list[now].key!=x) now = list[now].next;
return now;
}
//在key为x的元素后插入key为y的元素
bool insert_back(int x,int y){
if(tot+1>N) return false;
int now = find(x);
if(now==0) return false; //未找到key为x的元素,插入失败
//查找结束后,list[now]是key为x的元素
//新元素存放到数组中
list[++tot] = node(y,now,list[now].next);
//更新list[now]下一个元素list[list[now].next]的prev
//list[now].next是list[now]的下一个元素在list数组的存储下标
//list[list[now].next]就是list[now]的下一个元素
list[list[now].next].prev = tot;
//更新list[now]的next
list[now].next = tot;
return true;
}
//在key为x的元素前插入key为y的元素
bool insert_front(int x,int y){
if(tot+1>N) return false;
int now = find(x);
if(now==0) return false; //未找到key为x的元素,插入失败
//查找结束后,list[now]是key为x的元素
//新元素存放到数组中
list[++tot] = node(y,list[now].prev,now);
//更新list[now]上一个元素list[list[now].prev]的next
//list[now].prev是list[now]的上一个元素在list数组的存储下标
//list[list[now].prev]就是list[now]的上一个元素
list[list[now].prev].next = tot;
//更新list[now]的prev
list[now].prev = tot;
if(head==now) head = tot;
return true;
}
//删除key为x的元素
bool del(int x){
int now = find(x);
if(now==0) return false; //未找到key为x的元素,删除失败
//查找结束后,list[now]是key为x的元素
list[list[now].next].prev = list[now].prev;
list[list[now].prev].next = list[now].next;
if(head==now) head = list[head].next;
return true;
}
int main()
{
//生成上面图例的双向链表
list[++tot] = node(3,0,2);
list[++tot] = node(5,1,3);
list[++tot] = node(2,2,4);
list[++tot] = node(1,3,5);
list[++tot] = node(4,4,0);
printall();
insert_back(1,6);
//insert_front(3,6);
printall();
del(2);
printall();
return 0;
}
5.双向链表解决约瑟夫问题
约瑟夫问题同样可以用循环双链表来解决:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100;
//本例中记录第i个人的前一个人、后一个人的编号的结构体肯定存储在数组元素list[i]中
//所以结构体中不需要存储人的编号
struct node{
int prev,next;
node(){}
node(int prev,int next){
this->prev = prev;
this->next = next;
}
};
node list[N+10];
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
list[i] = node(i-1,i+1);
}
//构成循环双链表
list[1].prev = n;
list[n].next = 1;
int i = n; //i记录数数的人的编号,初始值设置为n,进入循环正好第1个人数数
while(list[i].next != i){
//m个人依次数数
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) i = list[i].next;
cout<<i<<" ";
//删除编号为i的元素
list[list[i].prev].next = list[i].next;
list[list[i].next].prev = list[i].prev;
}
return 0;
}
 NOIP学习小站
NOIP学习小站