前面小节我们学习了用结构体数组来存储链表,结构体中的prev和next“指针”其实是整数,指向的是上一个元素和下一个元素在数组中的存储下标。其实我们还可以在结构体中使用真正的指向上一个元素和下一个元素的指针来实现链表。
一、普通链表
1.使用结构体定义结点
可以在结构体内部设置一个指向该结构体的指针成员来指向链表的下一个结点(或者上一个结点),具体做法如下:
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *next; //结点的next指针,指向下一个node接点
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
node *head; //链表的head指针,指向链表的首结点
可知结构体node内部有一个node类型(与结构体名称相同)的指针next,用来指向链表中该结点的下一个结点。构造函数中将next设置成了一个特殊的空指针NULL。
2.生成链表
仍然是上节课引例中的链表,用这样的方式生成的链表结构如下:
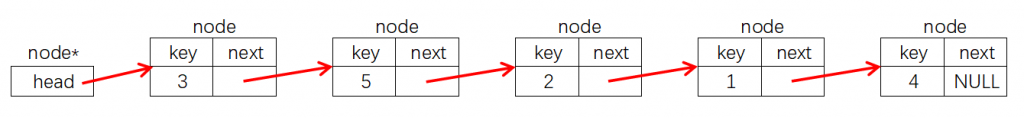
可以使用node *p = new node(n);这样“new +结构体构造函数”的方式生成一个指向结构体的指针,那么生成上述链表的代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *next; //结点的next指针,指向下一个node接点
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
node *head; //链表的head指针,指向链表的首结点
int main()
{
node *p,*q;
head = p = new node(3);
q = p;
p = new node(5);
q->next = p;
q = p;
p = new node(2);
q->next = p;
q = p;
p = new node(1);
q->next = p;
q = p;
p = new node(4);
q->next = p;
q = p;
//遍历链表的所有结点
p = head;
while(p!=NULL){ //条件p!=NULL可以简写成p(p不为NULL则条件成立)
cout<<p->key<<" ";
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
当然可以将结点的key存储在数组中,使用循环生成链表:
//正向建立链表
const int N = 5;
int a[N] = {3,5,2,1,4};
node *p,*q;
head = q = new node(a[0]);
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
p = new node(a[i]);
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
//反向建立链表
const int N = 5;
int a[N] = {3,5,2,1,4};
node *p,*q;
q = new node(a[N-1]);
for(int i=N-2;i>=0;i--){
p = new node(a[i]);
p->next = q;
q = p;
}
head = p; //head = q;亦可
3.查找结点
查找key为x的结点,返回指向结点的指针,找不到返回NULL(注意此时函数的返回值是指针):
node* find(int x){ //返回key为x的结点的指针(找不到返回NULL)
node *p = head;
while(p && p->key!=x) p = p->next;
return p;
}
4.插入结点
在结点指针p后面插入一个key为y的结点,只需要执行下图所示①②③三步操作:
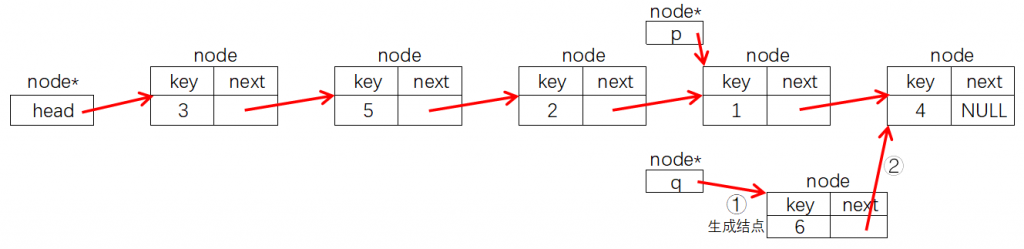
node *q = new node(y);②:
q->next = p->next;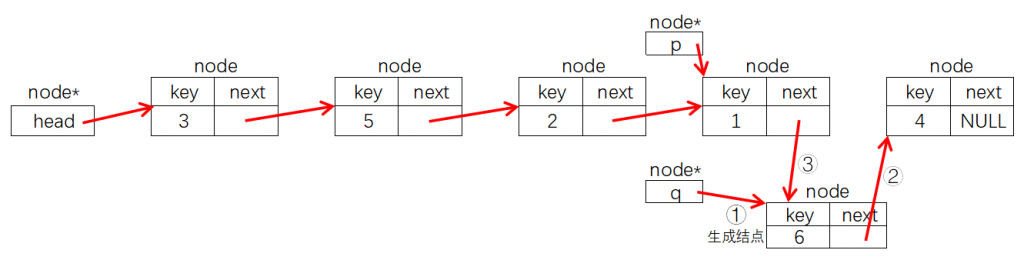
p->next = q;node *q = new node(y); q->next = p->next; p->next = q;
5.删除结点
删除结点指针p后面的结点,只需要执行下图所示①②③三步操作:

node *q = p->next;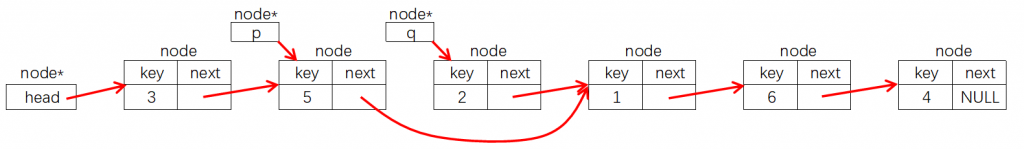
p->next = q->next;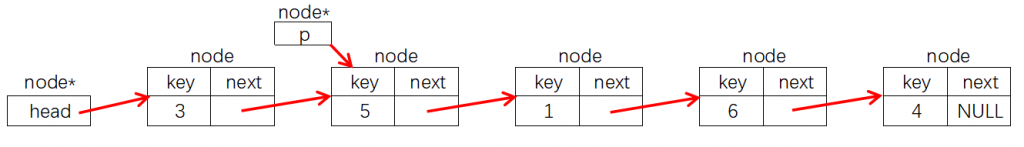
delete q;释放q指向的node结点内存node *q = p->next;
if(q) {
p->next = q->next;
//delete q;
}
6.完整测试程序
完整的测试代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *next; //结点的next指针,指向下一个node接点
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
node *head; //链表的head指针,指向链表的首结点
//遍历链表的所有结点
void printall(){
node *p = head;
while(p){
cout<<p->key<<" ";
p = p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//查找key为x的结点,返回指向结点的指针
node* find(int x){
node *p = head;
while(p && p->key!=x) p = p->next;
return p;
}
int main()
{
//正向建立链表
const int N = 5;
int a[N] = {3,5,2,1,4};
node *p,*q;
head = q = new node(a[0]);
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
p = new node(a[i]);
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
printall();
p = find(1);
if(p){
//在p后插入新结点
node *q = new node(6);
q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
}
printall();
p = find(5);
if(p){
//删除p的下一个结点
node *q = p->next;
if(q) {
p->next = q->next;
//delete q;
}
}
printall();
return 0;
}
7.使用链表解决约瑟夫问题
和上一小节一样,用循环链表解决约瑟夫问题:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *next; //结点的next指针,指向下一个node接点
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
node *head,*p,*q;
head = q = new node(1);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
p = new node(i);
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
p->next = head; //构成循环链表
//循环开始前p、q均指向最后一个结点
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
//前m-1个人数数
for(int i=1;i<m;i++) p = p->next;
q = p->next; //第m个人数数
cout<<q->key<<" ";
p->next = q->next;
}
return 0;
}
二、双向链表
单链表可以快速实现在某个结点后插入新结点或者删除某个结点后的结点,但是如果要在结点前插入新结点或者删除某个指定结点就有难度了,这个时候可以使用双链表:
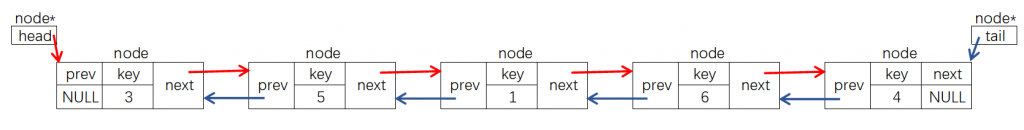
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *prev,*next;
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->prev = NULL; //NULL是空指针
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
node *head,*tail; //链首指针和链尾指针
int main()
{
const int N = 5;
int a[N] = {3,5,2,1,4};
node *p,*q;
head = q = new node(a[0]);
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
p = new node(a[i]);
p->prev = q;
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
tail = p;
//遍历链表的所有结点
p = head;
while(p){
cout<<p->key<<" ";
p = p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
//从链尾反向遍历链表所有结点
p = tail;
while(p){
cout<<p->key<<" ";
p = p->prev;
}
return 0;
}
在指针结点p后插入key为y的结点、在指针结点p前插入key为y的结点、删除指针结点p的参考代码如下,大家可以参照下图自行分析:
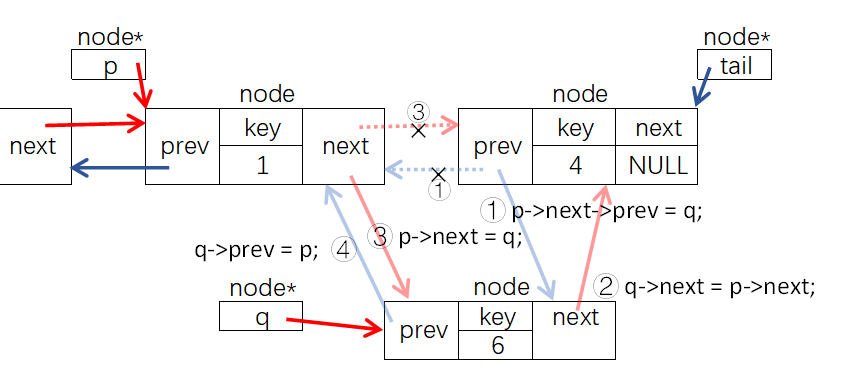
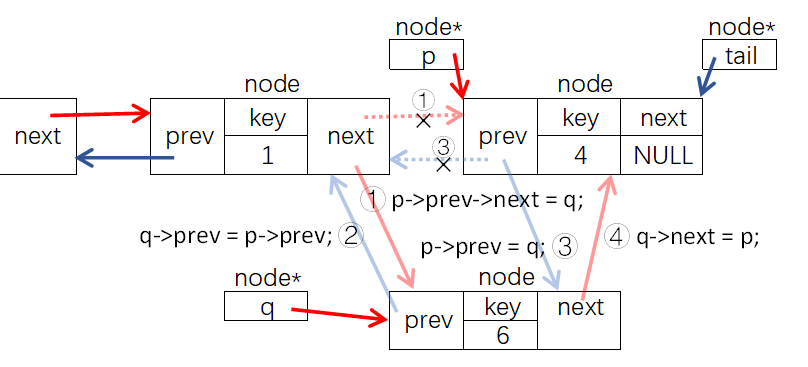
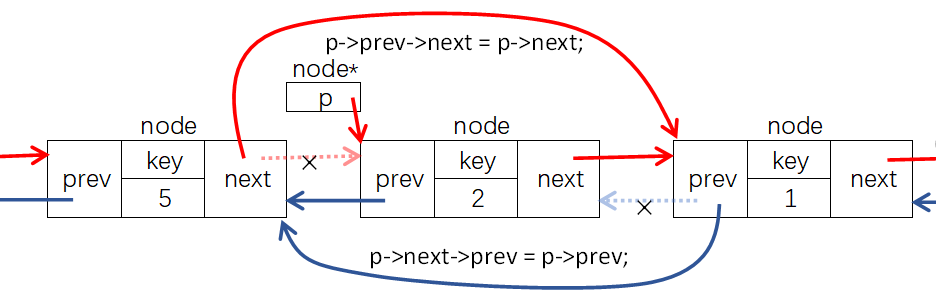
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *prev,*next;
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->prev = NULL; //NULL是空指针
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
node *head,*tail; //链首指针和链尾指针
//遍历链表的所有结点
void printall(){
node *p = head;
while(p){
cout<<p->key<<" ";
p = p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//从链尾反向遍历链表的所有结点
void rprintall(){
node *p = tail;
while(p){
cout<<p->key<<" ";
p = p->prev;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//查找key为x的结点,返回结点指针
node* find(int x){
node *p = head;
while(p && p->key!=x) p = p->next;
return p;
}
//从链尾反向查找key为x的结点,返回结点指针
node* find(int x){
node *p = tail;
while(p && p->key!=x) p = p->prev;
return p;
}
//在指针结点p后插入key为y的结点
void insert_back(node *p,int y){
node *q = new node(y);
if(p->next) p->next->prev = q;
else tail = q;
q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
q->prev = p;
}
//在指针结点p前插入key为y的结点
void insert_front(node *p,int y){
node *q = new node(y);
if(p->prev) p->prev->next = q;
else head = q;
q->prev = p->prev;
p->prev = q;
q->next = p;
}
//删除指针结点p
void _delete(node *p){
if(p==head) head = p->next;
if(p==tail) tail = p->prev;
if(p->prev) p->prev->next = p->next;
if(p->next) p->next->prev = p->prev;
//delete p;
}
int main()
{
const int N = 5;
int a[N] = {3,5,2,1,4};
node *p,*q;
head = q = new node(a[0]);
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
p = new node(a[i]);
p->prev = q;
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
tail = p;
printall();
rprintall();
p = find(4);
if(p) insert_front(p,6);
printall();
rprintall();
p = find(2);
if(p) _delete(p);
printall();
rprintall();
return 0;
}
同样地,可以使用循环双链表解决约瑟夫问题:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//借助结构体定义链表的结点
struct node{
int key;
node *prev,*next;
node(){} //无参构造函数
node(int key){ //有参构造函数
this->key = key;
this->prev = NULL; //NULL是空指针
this->next = NULL; //NULL是空指针
}
};
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
node *head,*p,*q;
head = q = new node(1);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
p = new node(i);
p->prev = q;
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
//构成循环链表
p->next = head;
head->prev = p;
//循环开始前p指向最后一个结点
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
//m个人依次数数
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) p = p->next;
cout<<p->key<<" ";
//删除结点p
p->prev->next = p->next;
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}
return 0;
}
 NOIP学习小站
NOIP学习小站